There may be times when you want to restrict what commands a user can issue when they attempt to login over an SSH connection. Instead of executing the users shell, you can instead execute a custom script that limits the user to a specific set of commands. This is known as ForceCommand.
There are two ways one can choose to use this. Today, I’ll describe a scenario where you don’t have permissions to modify the SSH server config (/etc/ssh/sshd_config) but still want to enforce specific commands for certain users (identified by their SSH key).
First, create a script somewhere that you have write permissions. We’ll reference this later in our config. Here’s a quick example to get you started that only allows you to get a process list (ps -ef) and print system statistics (vmstat).
#!/bin/sh
# script: /home/shane/bin/wrapper.sh
case "$SSH_ORIGINAL_COMMAND" in
"ps")
ps -ef
;;
"vmstat")
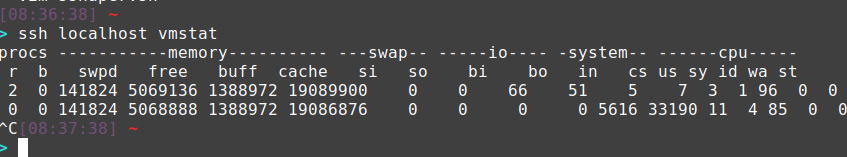
vmstat 1 100
;;
*)
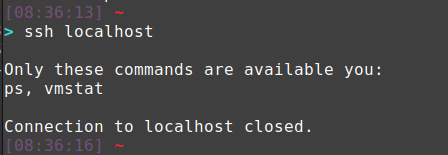
echo "Only these commands are available to you:"
echo "ps, vmstat, cupsys stop, cupsys start"
exit 1
;;
esac
Be sure to set the script to be executable.
chmod +x /home/shane/bin/wrapper.sh
Now, we just need to edit our ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file to reference this script. Note, you could create multiple scripts and assign them to different users’s SSH keys to allow different commands.
command="/home/shane/bin/wrapper.sh",no-port-forwarding,no-agent-forwarding ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC....snip...
Here’s how it would look in practice.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.